YEAR 7 HUMANITIES - ANCIENT CHINA
INTRODUCTION
Ancient China was one of the most amazing civilisations in history. In the 5th century BCE it was made up of several rival kingdoms. These were conquered by the king of the state of Qin, who became the First Emperor in 221 BCE. The Chinese people became unified as one kingdom, which lasted for about 2000 years. It was the most advanced civilisation the world had ever seen.
Under the Chinese kingdom, education was highly prized, and the arts, especially music and painting, grew and flourished. The Ancient Chinese were also great scientists. Their invention of cast iron and gunpowder were centuries ahead of the rest of the world.
ANCIENT CHINESE SOCIAL STRUCTURE
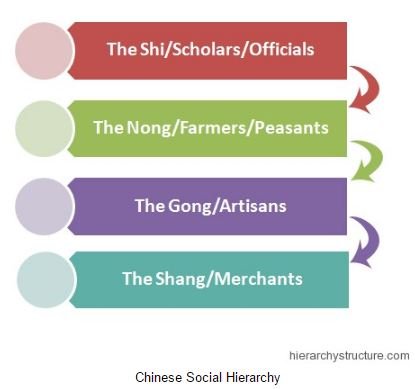
Social structure hierarchies were prevalent in most of the parts of the world. China also practised a social hierarchical structure in its societies that were divided into classes. The social classes of ancient China can be classified into four major categories. These were shi, nong, gong and shang.
QIN AND HAN DYNASTIES
Qin dynasty: Shihuangdi. [Image]. In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved from http://media1.school.eb.com.au/eb-media/24/102324-050-1776A8D2.jpg
INTRODUCTION
Scholars divide China's history into several periods, normally referred to as dynasties. The dynasties were the families or sets of rulers who governed China during that period.
Roberts, Jeremy. "Dynasties, Chinese." Chinese Mythology A to Z. Facts On File, 2004.Ancient and Medieval History Online. http://db.corpus.wa.edu.au/login?url=http://online.infobase.com.db.corpus.wa.edu.au/Auth/Index?aid=102119&itemid=WE49&articleId=235106
USEFUL WEB LINKS
THE GREAT WALL
INTRODUCTION
Beginning in 324 BCE three northern Chinese states with nomadic neighbours—Qin (Ch'in), Zhao (Chao), and Yan (Yen)—began to build defensive walls. After Qin unified China in 221 BCE the first emperor ordered his most able general, Meng Tian (Meng T'ien), to connect these existing walls and extend them to form a unified system of defense. The result is the Great Wall of China.
USEFUL WEB SITES
GREAT WALL OF CHINA
WHAT MAKES THE GREAT WALL OF CHINA SO EXTRAORDINARY?
BRAINPOP
SILK AND SILK ROAD
INTRODUCTION
The ancient Chinese are believed to have discovered silk threads and learned how to weave them into strong and beautiful cloth before the middle of the third century BCE. For hundreds of years, the methods used in creating the material remained a secret; even after silk was exported to other countries, China had a monopoly on its production.
Roberts, Jeremy. "Silk in China." Chinese Mythology A to Z. Facts On File, 2004. Ancient and Medieval History Online. Retrieved from http://db.corpus.wa.edu.au/login?url=http://online.infobase.com.db.corpus.wa.edu.au/Auth/Index?aid=102119&itemid=WE49&articleId=235460
THE SILK ROAD : CONNECTING THE ANCIENT WORLD THROUGH TRADE
BRAINPOP
Username: corpus
Password: corpus2016
CONFUCIUS
INTRODUCTION
For more than 2,000 years, the people of China have been guided by the principles of Confucius. He was a teacher and philosopher who lived in ancient China. His teachings are known as Confucianism. Confucianism is a philosophy based on kindness, love and respect. Confucianism serves as a way of life, a source of values, as well as a social code for its followers.
Confucius. (2016). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved from http://school.eb.com.au.db.corpus.wa.edu.au/levels/high/article/440121
USEFUL WEB SITES
Year: Year 7
Subject: Humanities
Last Updated: Nov 8, 2021 2:04 PM